TREATMENTS
Our priority is to preserve natural pieces through treatmentsthat conservative dentistry offers us before extracting them.
Preventive dentistry will help us with all this through proper oral hygiene
and periodic dental and medical check-ups.
CONSERVATIVE AND PREVENTIVE DENTISTRY
Conservative dentistry
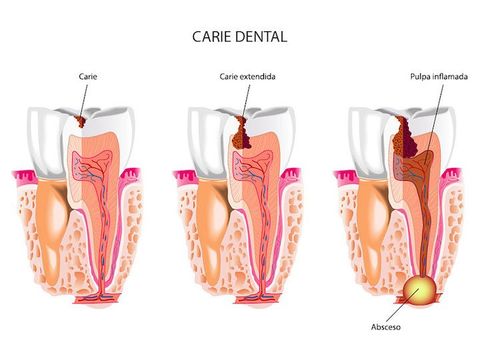
It is a branch of dental practice, whose objective is the healing and preservation of healthy teeth, avoiding whenever possible the extraction of damaged teeth. In this way, the damaged tissue is cleaned and acted upon, mainly we refer to cavities and trauma, and the affected parts are restored.
One of the main techniques used in conservative dentistry is the performance of fillings.
Preventive dentistry
It is based on constantly and correctly carrying out hygiene treatments and periodic dental and medical check-ups.
PERIODONTICS
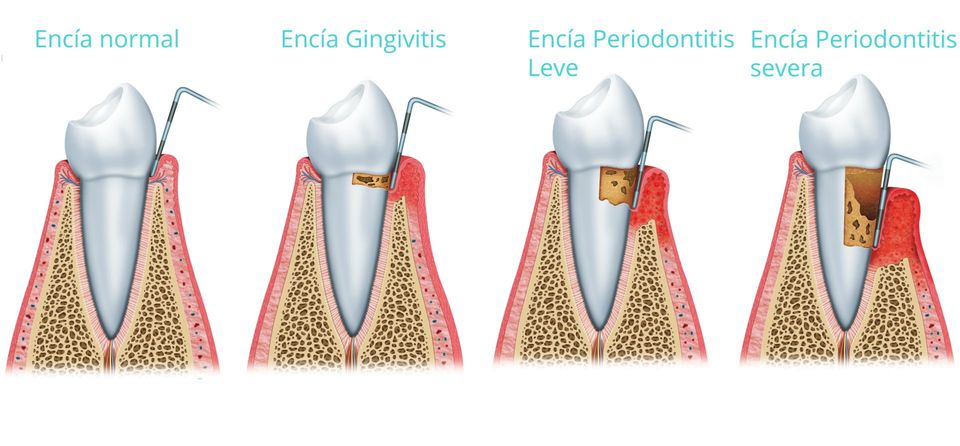
It is the dental specialty that studies the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of diseases and conditions that affect the tissues that support the teeth (gum, periodontal ligament, root cement and alveolar bone)
The main periodontal diseases that affect a dentition are periodontitis and gingivitis.
Periodontal disease manifests itself as gingivitis (inflammation and bleeding of the gum without affecting the bone) or periodontitis, where the bone that supports the tooth is destroyed. If it is not treated in time, it can cause tooth loss.
A periodontal treatment consists of the correction of the hygiene technique for the control of bacterial plaque, to the elimination of its triggering factors (dental calculi or tartar and periodontal pockets).
ENDODONTICS
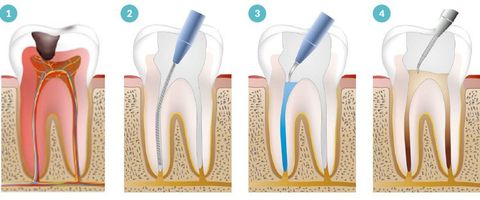
It is the treatment of root canals, so it refers to any therapy that is practiced in the dentin-pulp complex (dental pulp and its dentin) of a tooth. This technique consists of the total removal of the dental pulp and the subsequent filling and sealing of the pulp cavity with an inert material; and it is carried out with the aim of avoiding tooth extraction and maintaining its functionality.
ORAL SURGERY
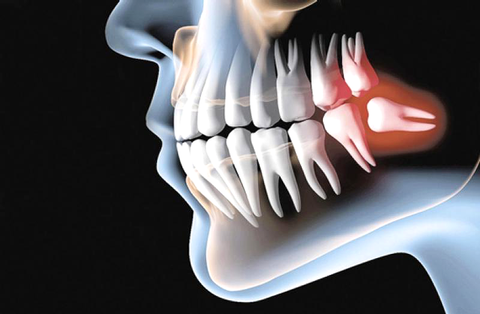
This specialty encompasses the diagnosis and surgical treatment of diseases that occur in the mouth, jaws and their tissues.
The oral surgeryincludes all types of extractions, removal of lesions and histological analysis of them
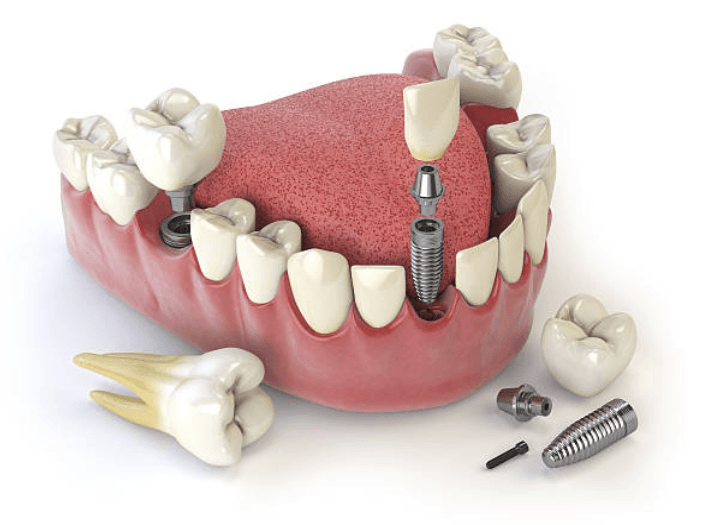
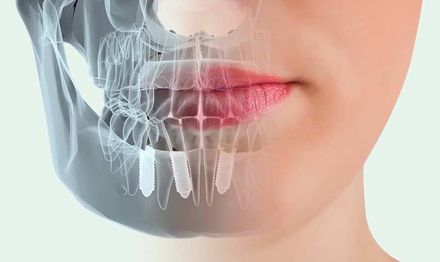
IMPLANTOLOGY
It is the branch of the odontology
which deals with replacing teeth lost due to different causes, using dental implants placed in the maxillary or mandibular bone.
Dental implants can be of different sizes, surfaces and materials. Prosthetic restorations are designed on the implants that will allow to restore the masticatory, phonetic and aesthetic functions of the patient. The choice of the type of implant that is placed in patients is made based on the diagnosis, prognosis and the interdisciplinary treatment plan determined by the dentist
Currently, most intraosseous implants are shaped like a dental root and the materials used for their manufacture are highly biocompatible, such as titanium, which allows a biologically stable union to the bone called Osseointegration.
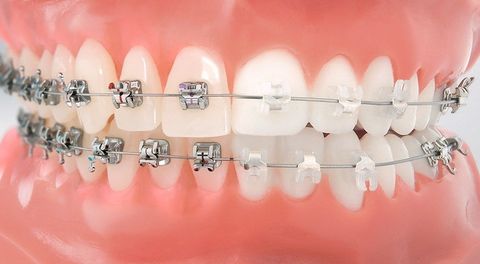
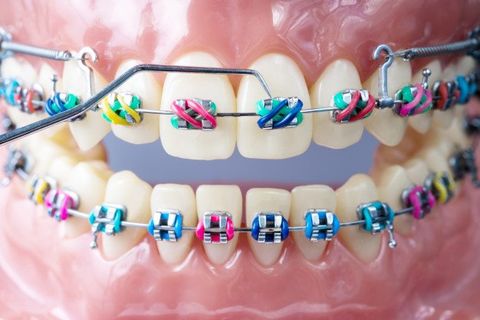
ORTHODONTICS AND ORTHOPEDICS
It is a dental specialty that studies, prevents and corrects developmental alterations, the shapes of the dental arches and the position of the jaws, in order to restore the morphological and functional balance of the mouth and face, also improving aesthetics. facial.
Hisfundamental objective is to treat and correct these defectsto keep the teeth in a healthy state and looking good, as improperly positioned teeth make oral hygiene difficult, they are prone to fall out early, suffer unusual wear, and cause tension and pain in the muscles involved in chewing.
Some of the most common conditions in orthodontics areoverbite, open bite, crossbite, scissor bite, deviated midline, crowding, among others.
There are many types of treatments both in orthopedics and orthodontics; in orthopedics there are fixed and removable appliances, which is determined based on the malocclusion that it presents. In orthodontics, the treatment can be carried out with brackets (conventional, aesthetic, self-ligating) or with aligners.
PROSTHETIC REHABILITATION
A dental prosthesis is an artificial element intended to restore the anatomy of one or more teeth, also restoring the relationship between the jaws, while returning the vertical dimension, and replenishing the teeth.
The support of the prostheses, that is, the structures of the mouth (teeth and periodontium) that will support the prostheses, must be carefully chosen, since both stability and retention will depend in part on good support. Occlusal forces must be taken into account so that the support is, as far as possible, the widest and best distributed in the mouth.
The prostheses can be:
• Toothed:
Those that are supported by the abutment teeth, or remnants, of the patient, which are natural teeth that he still has. The teeth can retain their entire structure, or they can be (in the vast majority of cases) teeth previously carved by the dentist. Tooth-supported are fixed prostheses
• Mucosupported:
Those that are supported on the alveolar process, in contact with the gum, which is a fibromucosal tissue. Fully mucosa-supported dentures are typical "dentures" (full resin dentures).
• Dentomucosupported:
Those that combine the two types of supports mentioned above, that is, they are supported both in the remaining teeth of the patient and in the alveolar process. They are metal prostheses, partial resin prostheses, and mixed prostheses.
• Implanted patients:
Those that are supported by surgical implants (implant-supported prostheses).
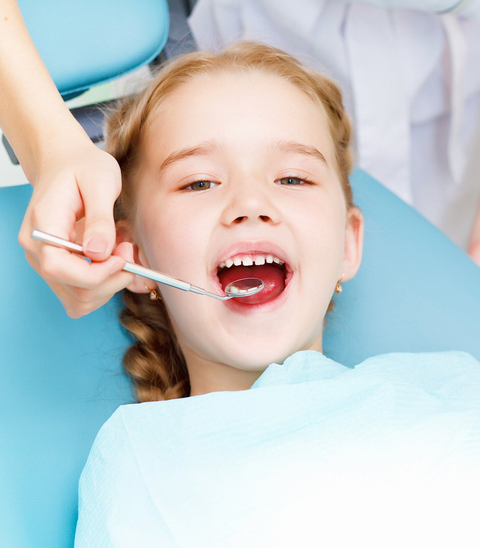
DENTISTRY PEDIATRICS
It is the branch of dentistry in charge of treating children. Thepediatric dentistHe will therefore be in charge of exploring and treating children. It is also in charge of detecting possible anomalies in the position of the jaws or teeth to refer to the orthodontist, an orthodontic specialist, and of doing a restorative treatment if needed. The restorative treatment mainly consists of treating trauma, using sealants that have the function of slightly filling the grooves and fissures of the teeth without hardly removing dental material to avoid possible cavities, and treating the cavities produced and their consequences.
The main difference between regular dentistry andpediatric dentistryin the treatment of cavities it is the presence of temporary or milk teeth in children which causes the treatment to change.

DENTAL AESTHETICS
Aesthetic or cosmetic dentistry is a specialty of dentistry that solves problems related to oral health and the aesthetic harmony of the mouth as a whole.
This branch or dental specialty aims to improve dental aesthetics or achieve a perfect smile through simple, painless, short treatments, that is, they do not require much time or many sessions and are very effective, since improvements or visible changes can be seen in very Little time.
The problems can help you solve, they are the following:
• Dental asymmetries:
They are not a problem of hygiene or health, they are a question of dental aesthetics. When a patient has dental asymmetries, it means that his teeth are crowded or uneven.
• Interincisor diastemas
they are the separation between the anterior teeth.
• Darkened or discolored teeth
• Neck cavities
which are those that occur near the gum and cause an unpleasant appearance.
• Dental fractures
The main cosmetic dentistry treatments are:
• Teeth whitening: It is one of the most requested treatments. Its objective is to remove the stains that darken the teeth. It is a relatively inexpensive treatment and offers very good results.
• Closure of diastema and correction of dental asymmetries:
This treatment is carried out to eliminate the gaps between the teeth. It is a technique that must be performed by a specialist. It is a more complex procedure than teeth whitening and therefore more expensive.
• Restoration of neck caries
• Use of aesthetic porcelain veneers
• Replacement of amalgams for restorations with composites
• Reconstruction of dental fractures




